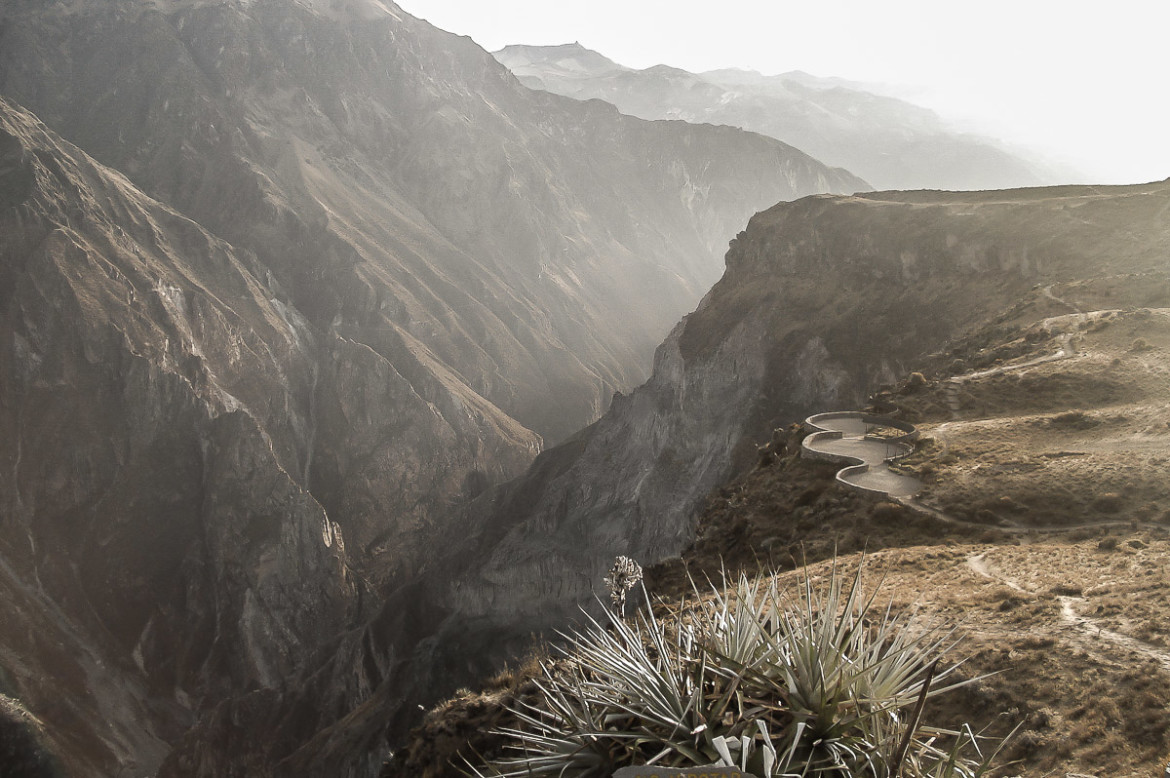

Colca Canyon
Colca Canyon is a canyon of the Colca River in southern Peru, located about 100 miles (160 kilometers) northwest of Arequipa.
With a depth of 10,725 ft (3,270 m), it is one of the deepest in the world, second in Peru after the Cotahuasi Canyon and more than twice as deep as the Grand Canyon in the United States. The Colca Valley is a colorful Andean valley with pre-Inca roots, and towns founded in Spanish colonial times, still inhabited by people of the Collagua and the Cabana cultures. The local people maintain their ancestral traditions and continue to cultivate the pre-Inca stepped terraces.

Train in Perù
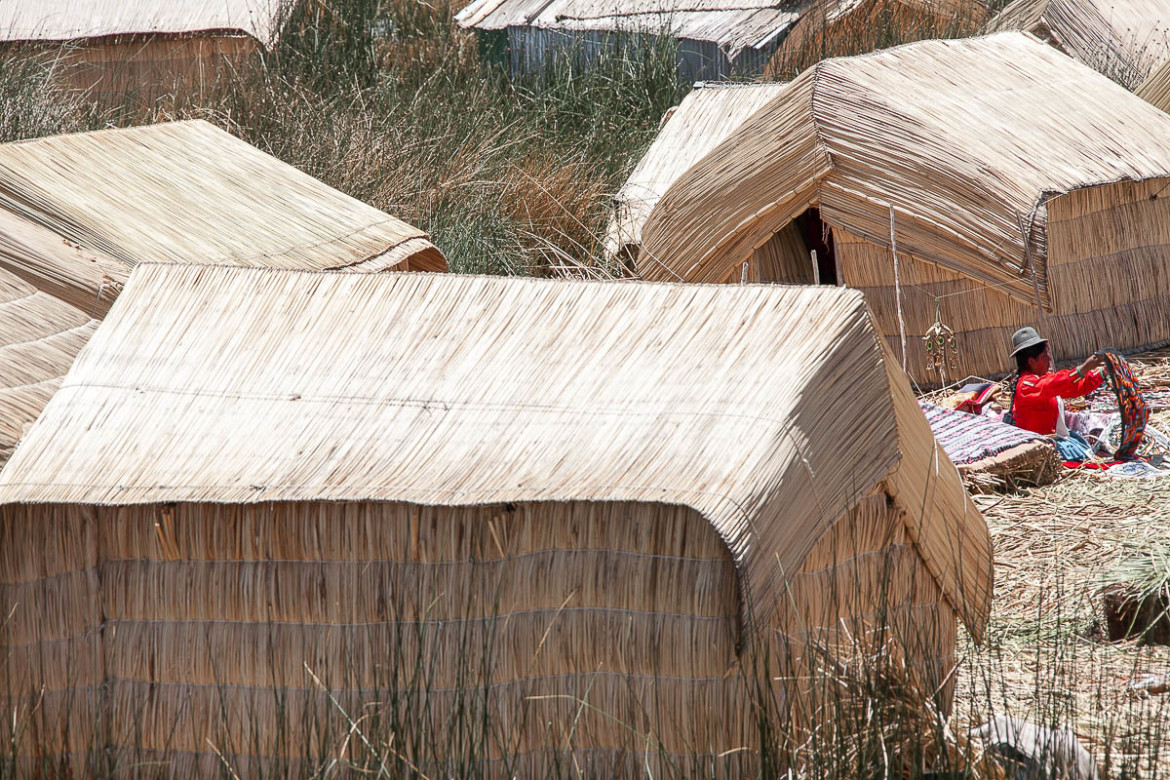

The Uros, Titicaca Lake, Perù
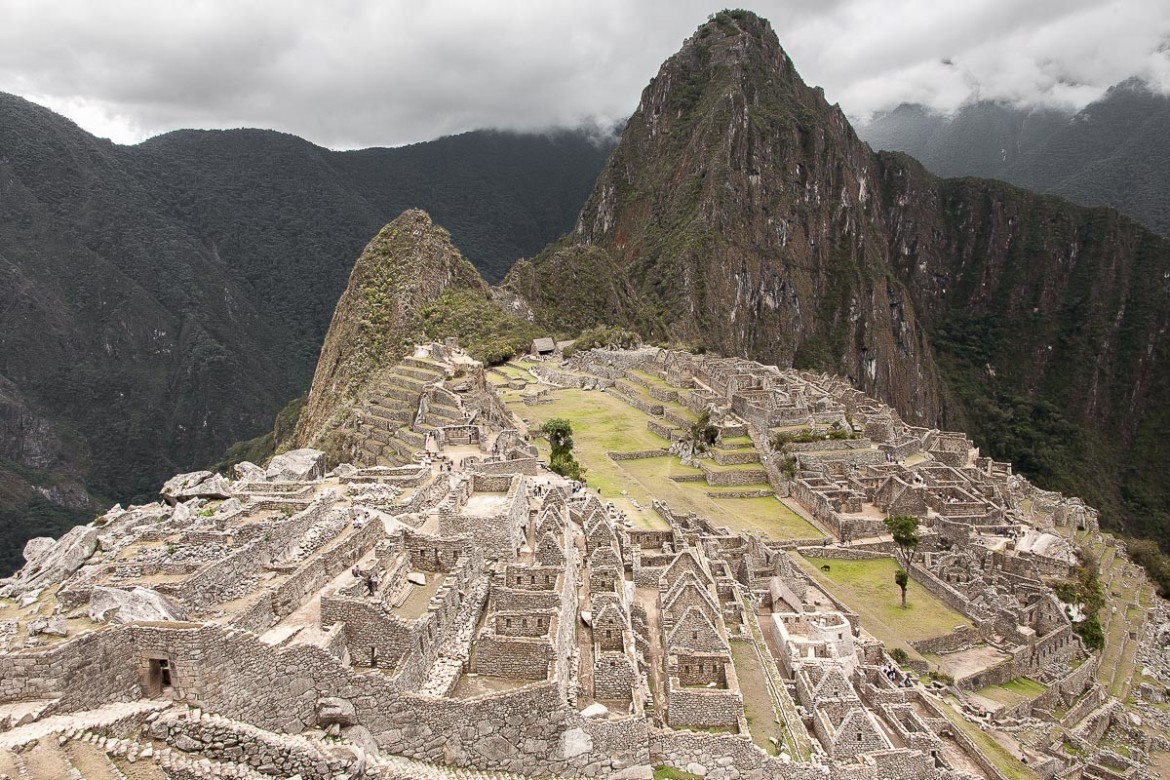

Machu Picchu
Machu Picchu is a 15th-century Inca site located 2,430 metres (7,970 ft) above sea level. It is located in the Cusco Region, Urubamba Province, Machupicchu District in Peru.
It is situated on a mountain ridge above the Sacred Valley which is 80 kilometres (50 mi) northwest of Cuzco and through which the Urubamba River flows. Most archaeologists believe that Machu Picchu was built as an estate for the Inca emperor Pachacuti (1438–1472). Often mistakenly referred to as the "Lost City of the Incas", it is the most familiar icon of Inca civilization.
The Incas built the estate around 1450, but abandoned it a century later at the time of the Spanish Conquest. Although known locally, it was not known to the Spanish during the colonial period and remained unknown to the outside world before being brought to international attention in 1911 by the American historian Hiram Bingham. Most of the outlying buildings have been reconstructed in order to give tourists a better idea of what the structures originally looked like. By 1976, thirty percent of Machu Picchu had been restored. The restoration work continues to this day.
Machu Picchu was declared a Peruvian Historical Sanctuary in 1981 and a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1983. In 2007, Machu Picchu was voted one of the New Seven Wonders of the World in a worldwide Internet poll.
Machu Picchu was built in the classical Inca style, with polished dry-stone walls. Its three primary structures are the Inti Watana, the Temple of the Sun, and the Room of the Three Windows.
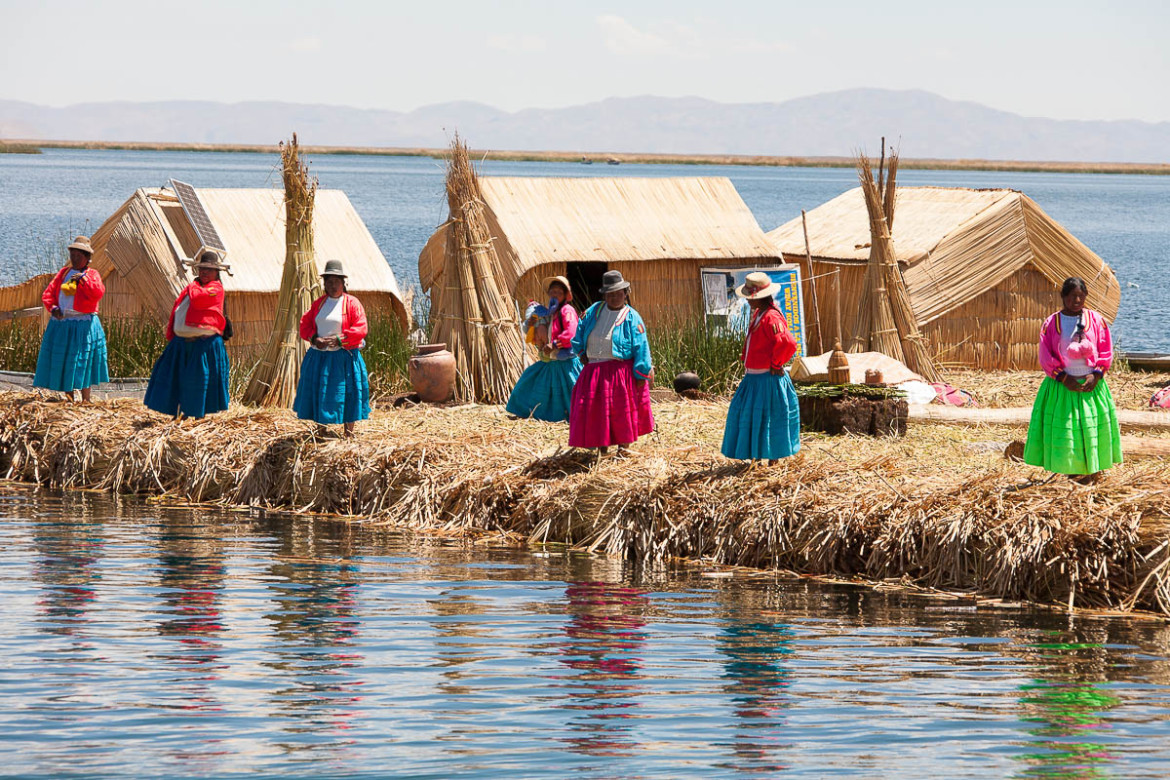

The Uros
The Uros descend from a millennial town that, according to legends, are "pukinas" who speak Uro or Pukina and that believe they are the owners of the lake and water. Uros used to say that they have black blood because they did not feel the cold. Also they call themselves "Lupihaques" (Sons of The Sun). Nowadays, Uros do not speak the Uro language, nor practice their old beliefs but keep some old customs.
The purpose of the island settlements was originally defensive, and if a threat arose they could be moved. The largest island retains a watchtower almost entirely constructed of reeds.
The Uros traded with the Aymara tribe on the mainland, intermarrying with them and eventually abandoning the Uro language for that of the Aymara. About 500 years ago they lost their original language. When conquered by the Inca empire, they had to pay taxes to them, and often were made slaves.

Isla del Sol, Perù
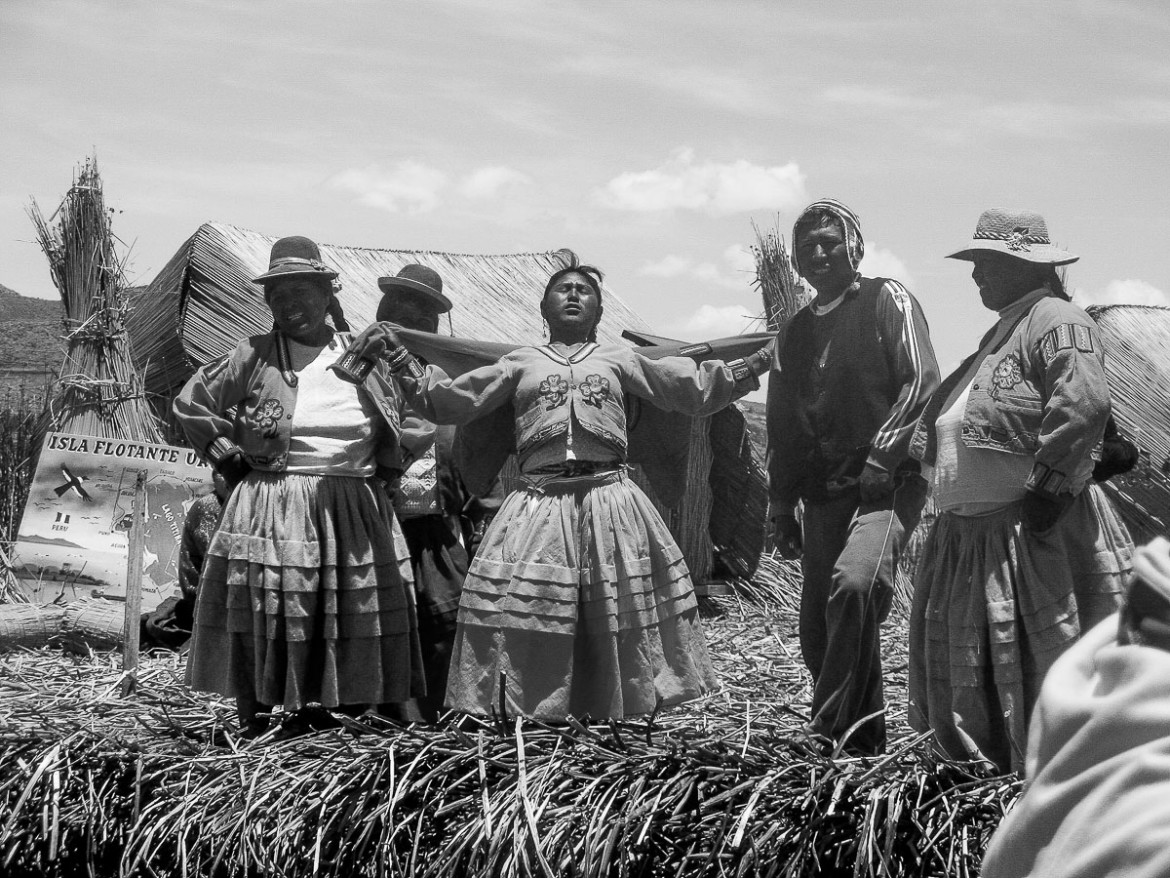

The Uros, Titicaca Lake, Perù
The Uros (Uru: Qhas Qut suñi) are a pre-Incan people who live on forty-two self-fashioned floating islands in Lake Titicaca Puno, Peru and Bolivia. They form three main groups: Uru-Chipayas, Uru-Muratos and the Uru-Iruitos. The latter are still located on the Bolivian side of Lake Titicaca and Desaguadero River.

Isla del Sol, Perù












Share On